Question 1
What is the output of the following Program, if input
value is 6?
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int index;
int val
= 44;
int[] a
= new int[5];
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter
the number");
index
= Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
a[index]
= val;
}
catch (InvalidCastException ex)
{
Console.Write("Invalid
Cast Exception.");
}
catch (InvalidOperationException ex)
{
Console.Write("Invalid
Operation Exception.");
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
Console.Write("Index
was outside the bounds of the array.");
}
Console.Write("Hello");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Option:
1. Invalid Cast Exception.
2. Invalid Operation Exception.
3. Index was outside the bounds
of the array.
4. Index was outside the bounds
of the array.Hello
Correct Answer
4. Index was outside the bounds
of the array.Hello
Question 2
What is the output of the following Program?
class Program
{
public void Test<M>(M
arg)
{
Console.Write(arg);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p
= new Program();
p.Test("Hello");
p.Test(4.5f);
Console.Read();
}
}
Option:
1. It will be print: Hello4.5
2. It will be throw compile-time
exception.
3. It will be throw run-time
exception.
4. It will be print: Hello.
Correct Answer
1. It will print: Hello4.5
Question 3
What is the output of the following Program?
class Program
{
protected int count;
public Program()
{
count
= 0;
}
}
class Program1 : Program
{
public void Increment()
{
count
= count + 1;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program1 p
= new Program1();
p.Increment();
Console.Read();
}
}
Option:
1. Count variable should be mark
as public.
2. Count variable should be mark
as protected.
3. Program1 class can't not
inherit the Program class.
4. The Count variable will
increment by 1 but not print anything.
Correct Answer
4. The Count variable will
increment by 1 but not print anything.
Question 4
Hoe to read value from stack?
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stack<string>
numbers = new Stack<string>();
numbers.Push("one");
numbers.Push("two");
numbers.Push("three");
numbers.Push("four");
numbers.Push("five");
Console.Read();
}
}
Option:
1.
IEnumerator
e;
e =
numbers.GetEnumerator();
while
(e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
2.
IEnumerable
e;
e =
numbers.GetEnumerator();
while
(e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
3.
IEnumerator
e;
e =
numbers.IEnumerable();
while
(e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
4.
IEnumerable
e;
e =
numbers.IEnumerable();
while
(e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
Correct Answer
1.
IEnumerator
e;
e =
numbers.GetEnumerator();
while
(e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
Question 5
class Program
{
public delegate int PrintDelegate(int i);
public int Print(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
return i;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p
= new Program();
PrintDelegate pd
= new PrintDelegate(ref p.Print);
pd(5);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Output:
5
Question
6
Which
data Web controls is best in performance over DataGrid, DataList, and Repeater?
Correct
Answer
1.
Repeater is best performance over DataList and DataGrid.
2.
DataList is best performance over DataGrid.
Conclusion
The
Repeater does boast the best performance of the three data Web controls. Its
performance is comparable to the DataList's, but noticeably better than the
DataGrid's.
For
Ref.
Refer
Link
Question
7
What
is the Default Mode for Session State?
SqlSerevr
StateServer
InProc
None
All
Above
Correct
Answer
InProc
Question
8
What
is the output of below join?
CREATE
TABLE #TABLE1(ID INT)
CREATE
TABLE #TABLE2(ID INT)
INSERT
INTO #TABLE1 VALUES(1)
GO
3
INSERT
INTO #TABLE2 VALUES(1)
GO
2
SELECT
* FROM #TABLE1
SELECT
* FROM #TABLE2
SELECT
*
FROM
#TABLE1 A
INNER
JOIN #TABLE2 B ON A.ID=B.ID
Correct
Answer
6
Rows
Question 9
What is the output of the following Program?
class BaseClass
{
public BaseClass()
{
Console.WriteLine("Base
Class Constructor.");
}
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Base
Class Method.");
}
}
class Program : BaseClass
{
public Program()
{
Console.WriteLine("Derived
Class Constructor.");
}
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Derived
Class Method.");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BaseClass b
= new Program();
b.Print();
Program p
= new Program();
p.Print();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Correct
Answer
Base
Class Constructor.
Derived
Class Constructor.
Base
Class Method.
Base
Class Constructor.
Derived
Class Constructor.
Derived
Class Method.
Question 10
CREATE TABLE #OLD_EMP
(
EmpId Varchar(5),
EmpName Varchar(50),
DeptId int
)
insert into #OLD_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E001','Name 1','1')
insert into #OLD_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E002','Name 2','1')
insert into #OLD_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E003','Name 3','1')
insert into #OLD_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E004','Name 4','1')
CREATE TABLE #NEW_EMP
(
EmpId Varchar(5),
EmpName Varchar(50),
DeptId int
)
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E001','Name 1','3')
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E002','Name 2','3')
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E003','Name 3','3')
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E004','Name 4','3')
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E005','Name 5','5')
insert into #NEW_EMP(EmpId,EmpName,DeptId)values('E006','Name 6','6')
CREATE TABLE #Department
(
DeptId int,
DeptName Varchar(50)
)
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('1','IT')
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('2','Finance')
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('3','Marketing')
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('4','Sales')
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('5','Services')
insert into #Department(DeptId,DeptName)values('6','Management')
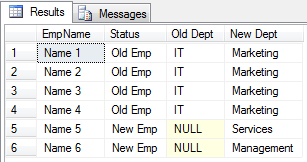
select * from #OLD_EMP
select * from #NEW_EMP
select * from #Department
Case Scenario:
I have Old Employee Table and Now I have created
the New Employee Table. In New Employee Table I
have shifted the all Old Employee Table records into it. But
those are old employee there department is IT in Old
Employee Table. But, In New Employee Table those are old
employee there department is Marketing.
Write a query to select employee name, if the employee is old then
selected as 'Old Emp' otherwise 'New Emp', old department of employment and new
department of the employee.
Query:
select
ne.EmpName,
case when oe.DeptId=dept2.DeptId then 'Old Emp' else 'New Emp' end 'Status',
dept2.DeptName'Old Dept',
dept1.DeptName'New Dept'
from #NEW_EMP ne
left join #OLD_EMP oe on ne.EmpId=oe.EmpId
left join #Department dept1 on ne.DeptId=dept1.DeptId
left join #Department dept2 on oe.DeptId=dept2.DeptId
Question 11
A class inherits from 2 interfaces and both the interfaces have
the same method name. How should the class implement the method for both the
interfaces?
We need to use explicit interface implementation technique to fix
it.
Or
We need to use Interface reference variable implementation
technique to fix it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExplicitInterface
{
interface ISayHello1
{
void SayHello();
}
interface ISayHello2
{
void SayHello();
}
class Program : ISayHello1, ISayHello2
{
void ISayHello1.SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello
from ISayHello1 interface");
}
void ISayHello2.SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello
from ISayHello2 interface");
}
static void Main(string[]
args)
{
//
Explicit interface implementation
Program p
= new Program();
((ISayHello1)p).SayHello();
((ISayHello2)p).SayHello();
//
Interface reference variable implementation
ISayHello1 p1
= new Program();
p1.SayHello();
ISayHello2 p2
= new Program();
p2.SayHello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Note:-
Access modifiers are not allowed on explicitly implemented
interface members.



No comments:
Post a Comment